Solutions in Acrylics
Solutions in Acrylics
Recycling of PMMA (acrylic glass)
Plastics are not all the same. PMMA makes a difference
While many plastics are used in disposable articles like food wrapping, bottles or packaging with very short life time, PMMA is not used in such products, but predominantly in high quality applications with extended life time expectations of 20 to 50 years.
Examples are widespread:
- transparent noise barriers
- public oceanarium and submarine windows,
- weathering protection films for traffic signs, window frames or building façade panels
- helicopter canopies and passenger cabin windows.
PMMA is accountable for only less than 1% of plastic waste in Germany and burns to CO2 and water without generating toxic gases.
However, PMMA is much to precious to be burnt.
Besides its versatility to match various different high end application requirements, acrylic glass has another feature that distinguishes it from many other polymers: acrylic glass is almost completely recyclable, both by regranulation of extruded acrylic glass and return to the production cycle, and by depolymerization of cast or extruded material, which re-generates the monomer methyl methacrylate (MMA). The MMA can then be used to make new products without using fossil resources.
There are two types of PMMA / acrylic glass
Extruded or injection molded PMMA
Thermoplastic molding compounds (granules) are used in the manufacturing process, which melt in the extruder. The molecular weights of the molding compounds are adjusted in such a way that the melt viscosity is optimal for further processing. The melt is extruded into films or sheets or injection molded into a molded part.
Recycling of extruded PMMA...
...is done by grinding production residues and returning them to the manufacturing process, in which the ground material is melted again together with the virging molding compound.
This process has been used for years to optimize volume flows and keep raw material costs low.
The extrusions manufacturing process allow for the use of up to 80% recycling material, depending on quality requirements of the application.
cast PMMA (sheets and blocks)
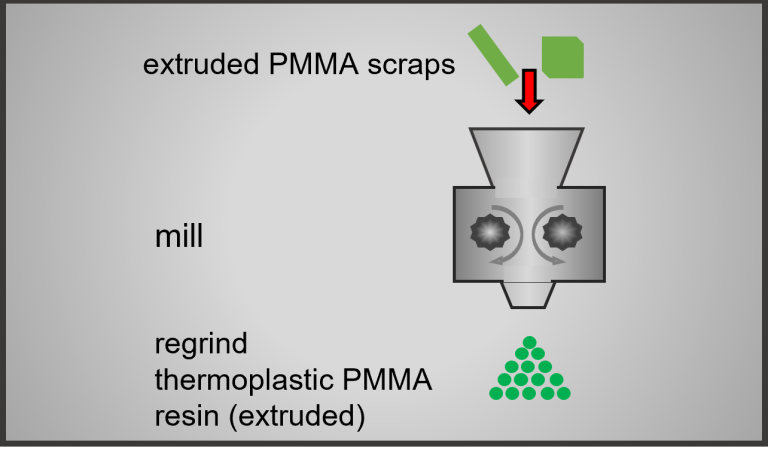
Re-granulation
Extruded PMMA scraps are milled to a process compatibe size and fed back into the production process.
Cast sheets and blocks are produced by direct polymerisation of the liquid monomer MMA between glass plates in a batch process. Cast PMMA sheets and blocks have a very high molecular weight. Although they are thermoplastic and can be thermoformed, cast PMMA CANNOT be melted because the polymer is decomposing thermally beforehand. Recycling by grinding and melting is therefore not possible with cast acrylic glass (PMMA).
Recycling of cast PMMA / acrylic glass
The manufacturing process of cast acrylic sheets from the liquid monomer MMA is a reversible equilibrium process. The monomer can therefore be recovered again by raising the temperature to near the so-called ceiling temperature (475°C). The monomer is gaseous at this temperature and can be separated by distillation and cooling. Traditionally, pyrolysis is carried out in batches using molten lead as the heat transfer medium (400° to 450°). However, this process is not very energy efficient and using molten lead has potential risks.
A much more technically advanced process uses a continuous, high-friction, heat-traced twin-screw extruder. This process is more energy efficient, more flexible, self-cleaning and delivers MMA in very good yield and quality.
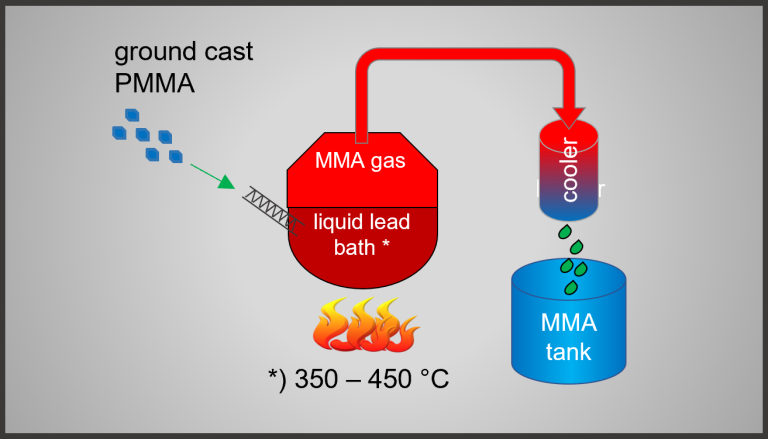
Lead bath process
Pyrolysis of cast PMMA in a molten lead bath and distillation of the monomer MMA
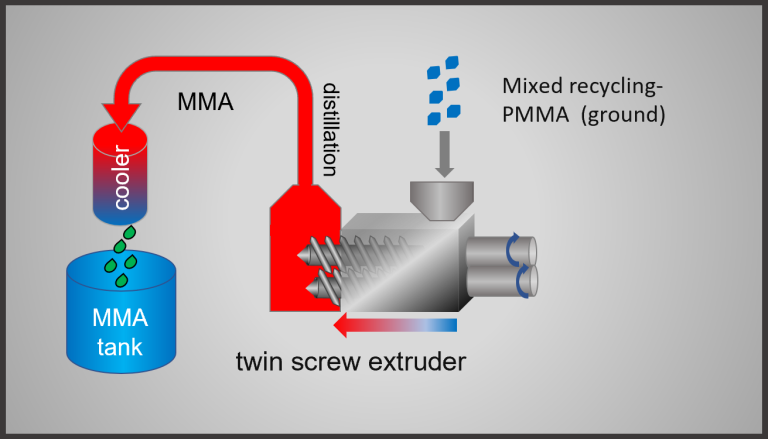
Continuous de-polymerisation
continuous pyrolysis of extruded and/or cast PMMA scraps in a Coperion twin-screw extruder
Renov8 has signed a contract in 2022 to buy a complete Coperion line for the continuous depolymerisation of cast and extruded PMMA in a twin screw extruder with integrated destillation of the monomer MMA.
This investment establishes the company as a first mover to commercialize this state-of-the art technology.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte überprüfen Sie die Details in der Datenschutzerklärung und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.